E-Coating Process: How it Works & Best Practices
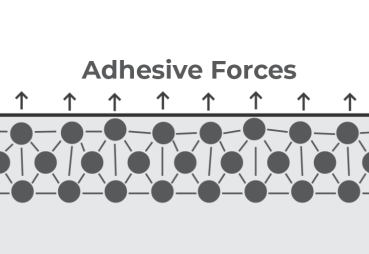
The e-coating process, also known as electrocoating, is a highly reliable method for protecting metal parts against corrosion, UV exposure and wear. By understanding how e-coating works and how to optimize it, you can ensure optimal throughput, reduce defects, and achieve high-quality coatings.